Part 11 : Following along MIT intro to deep learning
Abhijit Ramesh / April 22, 2021
8 min read • ––– views
Towards AI for 3d Content Creation
Introduction
A lot of advancements has been made in the field of AI as we know but also these advancements have been a support for advancements in the field of 3d Content creation with the support of AI.
This video is created with the help of Omniverse. All the content that is rendered in the video is rendered in real-time compared to the traditional rendering approaches.
3D Content
3D content is almost everywhere these days,
- Architecture - Designers model rooms and spaces that are to be build using 3d modelling
- Gaming - All latests games that are available are build using 3D
- Films - Most of the latest films that we watch these days have lot of graphics that are rendered 3D content
- VR - Characters in VR are rendered using 3D graphics
- Healthcare
- Robotics - This is an especially exciting one since it is used for creating simulations which can be used by AI to learn from these simulated environments and these learning can be applied to the real world.
In the 3d world most of the characters objects are already labeled this is very helpful to test and train these AI models as all the ground truth is already labelled and once they prove good in testing in these simulations they can be moved to the real world for more testing.

The new idea is that if we can simulate cities itself for training these robots, It does not just look good from a satellite view but also has good details in street level so that they have very good performance when training and testing AI. The problem is that doing this manually would take a lot of time.

The game GTA 5 took a team of 1000 engineers working full time over 3 years to create along with 250,000 photographs and many hours of video footage to that could give them the idea of projecting Los Angeles. AI can help here.
AI for 3D Content Creation
This that AI can learn to synthesise are
- Worlds → The scene composition
- Scene Layout → How are the objects in the scene placed
- Assets → Objects in the scene and other elements in the scene
- Scenarios → Position and goals of actors
- Behaviour → How these actors are going to behave in the world
- Animation → How realistic the motion of the actors are
Synthesizing Worlds
The idea is that we can use some generative models to synthesise scenes for the world from images. So depending upon what part of the world we want to simulate we should be able to change the elements in the scenes. The way to approach this problem is by thinking about how games do scene composition.

Here a probabilistic grammar is constructed which would decide on how these elements should be rendered. Currently, the distribution according to which these elements are rendered is determined by the artist the idea is that we use AI to learn these distributions so that it can be generated automatically.
Scene composition

The paper Meta-Sim discusses how we can synthesise these scenes, It was already said that there are these Probabilistic grammar that are used to generate the scene graph these graphs are then passed down to a Distributed transformer which would generate the transformed scene graphs that is then rendered to generate synthetic scenes, these scenes have a probability distribution which is compared to the distribution of the real scenes using Maximum Mean Discrepancy and the back propagation is done as normal numerical values.
These tasks can actually be optimised using as task network.

For example, if we are doing object detection on these synthetic scenes we can train a task network here as well as on the real data and then backpropagate these scores back to the transformed scene graph and to the distribution transformer.
Training the distribution for the attributes are kind of like the easy part the hard part is to learn the structure of these graphs. So if we are moving to a different environment like a village how do we learn the structure of the graphs so that it represents the elements of a village.
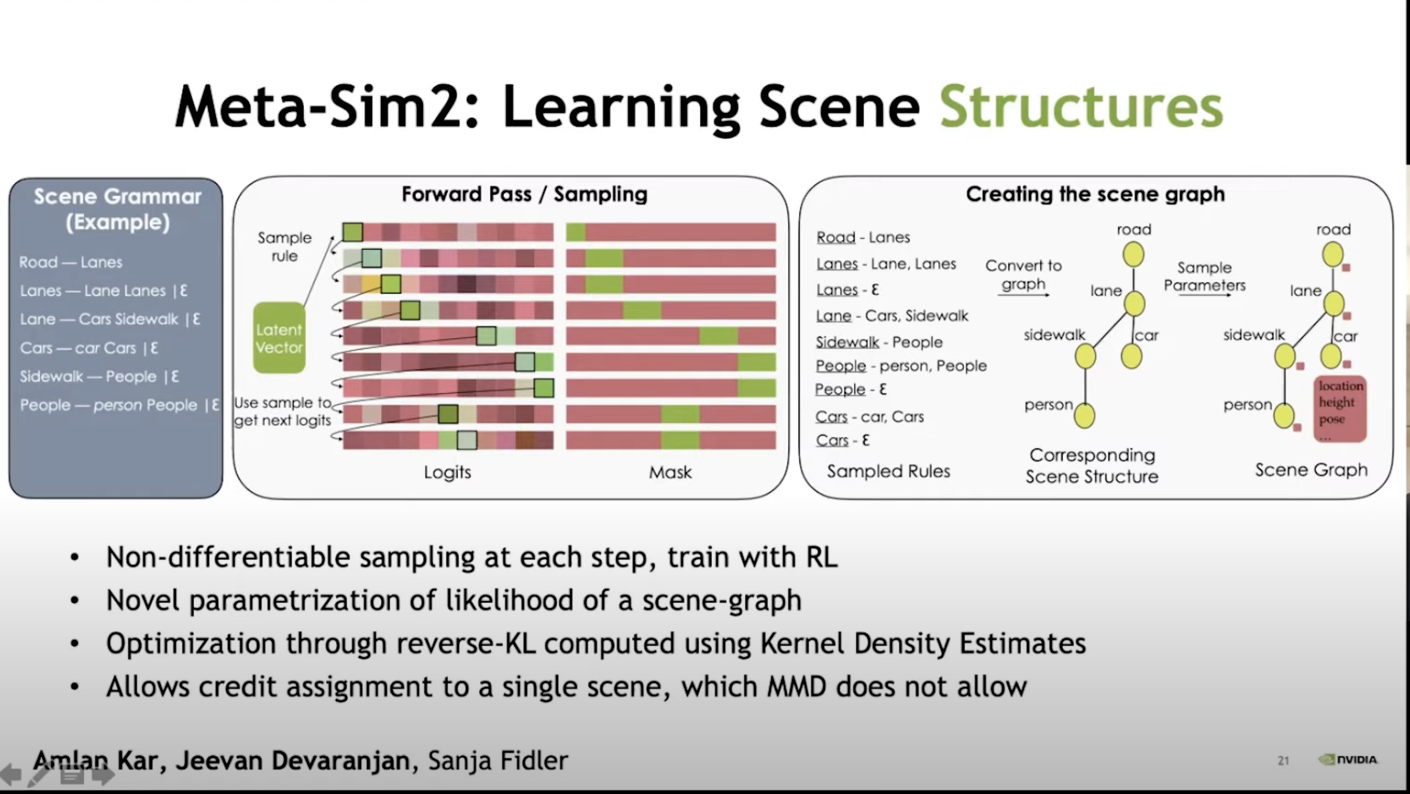
The idea is to train a network that will learn to sample from this probabilistic context-free grammar. We would be having some form of latent vector, we know from the scene graph what is the element we should be generating so we would mask the probabilities of the other elements. Then we would be able to know the correct probabilities for the next symbol we should be sampling. Each step this would be generating a rule until it reaches a terminal state where we can stop sampling. This would be generating a new graph and using the technique discussed above we can augment the rendering of the scene. This help us to generate the actual structure of the scene as well as the attributes in that scene.
So how does this result in ?

The prior is set purposefully to perform really bad, KITTI is a real world driving dataset and the learned model actually performs similar to this dataset.
This model can be evaluated by sampling from this model.

Synthesizing Medical Data

Medical data is very hard to come by this is where generating such data would be extremely helpful similar to how we generate the driving data this can also be done.
Recovering rules of the world
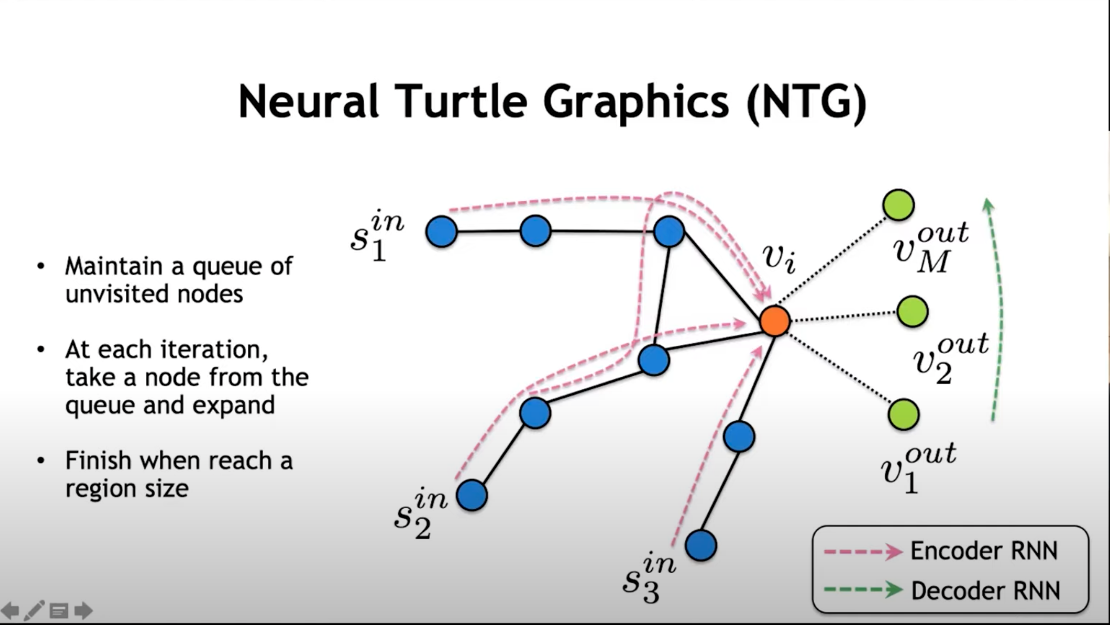
Now that we have generated the environments we should be able to generate the rules as well for these environments this can be done by considering roads as graphs with nodes are control points and edges as road segments

The idea here is to maintain a queue of unvisited nodes and then at each iteration take a node from the queue and expand and when the region size is reached we finish the iteration.
Object Creation
Most of these things have now be generated but again generating objects is also a hard task the artist still has to work on this, even though many of these are available online it is not a good idea to buy or get from online these 3d objects because for a big project this could not be the best solution.
So in order to solve this task AI is used to take pictures and synthesise 3D content from that pictures.

Graphics via differentiable rendering
The idea in graphics rendering is that there is a mesh, some lighting and a texture and this is passed on to a rendered to produce an image. But if we are able to make the graphics rendered differentiable we can say the opposite that given an image we are able to produce mesh, light and texture.


This bottleneck model is used to do exactly that, the neural network would produce the 3d components and these components are passed to a rendered where it will produce a rendered image this image is compared to the input image to find the loss which can be propagated back to the network. The 3d components are sent to a renderer because we don't have the ground truth for each of these objects.

Data Generation
Generating the data should also be a more smart approach we already know that we can use GAN's to generate images but here we do something different we still use a GAN but there would be a particular variable in the latent vector that controls the view point on the GAN this can be changed in order to obtain different view points of the object.

This is the data that can then be used to train the differentiable rendered model. This is implemented in the omniverse software which allows to convert the picture of car to a 3d object.
Neural Simulation
The idea here is that the AI would watch how a human would play a game and then try to recreate the game itself this is what Nvidia has done with the help of game gan.
The initial phase of this was to try and simulate how the game engine works.

This idea can then be transformed to simulating 3D games and even real worlds.
Currently Nvidia has a version that is training on real driving video.
3D deep learning library
Nvidia has developed a 3D deep learning library for everyone to use Kaolin.
Sources
MIT introtodeeplearning : http://introtodeeplearning.com/
Subscribe to the newsletter
Get emails from me about machine learning, tech, statups and more.
- subscribers